what would be your approach to finding the root cause of a problem?
What is Root Cause Analysis (RCA)?
Quality Glossary Definition: Root cause analysis
A root cause is defined as a factor that acquired a nonconformance and should be permanently eliminated through process improvement. The root cause is the core issue—the highest-level cause—that sets in motion the unabridged crusade-and-effect reaction that ultimately leads to the trouble(s).
Root cause assay (RCA) is defined as a collective term that describes a wide range of approaches, tools, and techniques used to uncover causes of problems. Some RCA approaches are geared more toward identifying true root causes than others, some are more general problem-solving techniques, and others simply offer back up for the core activity of root cause analysis.
- History of root cause assay
- Approaches to root cause analysis
- Conducting root crusade assay
- Root crusade analysis resources
History of Root Crusade analysis
Root cause assay can exist traced to the broader field of total quality management (TQM). TQM has adult in different directions, including a number of problem analysis, problem solving, and root crusade assay.
Root crusade assay is part of a more than general problem-solving process and an integral function of continuous improvement. Because of this, root cause assay is one of the core building blocks in an organization's continuous improvement efforts. It'southward important to note that root cause assay in itself will not produce any results; it must be made part of a larger problem-solving effort for quality improvement.
Approaches to Root Cause Analysis
There are many methodologies, approaches, and techniques for conducting root crusade analysis, including:
- Events and causal gene analysis: Widely used for major, single-event problems, such as a refinery explosion, this process uses evidence gathered chop-chop and methodically to establish a timeline for the activities leading upwards to the accident. Once the timeline has been established, the causal and contributing factors tin exist identified.
- Change analysis: This approach is applicative to situations where a organization'due south operation has shifted significantly. It explores changes fabricated in people, equipment, information, and more that may take contributed to the change in performance.
- Barrier analysis: This technique focuses on what controls are in place in the procedure to either preclude or detect a problem, and which might have failed.
- Management oversight and adventure tree analysis: One attribute of this approach is the use of a tree diagram to wait at what occurred and why it might accept occurred.
- Kepner-Tregoe Problem Solving and Conclusion Making: This model provides four distinct phases for resolving problems:
- Situation assay
- Problem assay
- Solution assay
- Potential trouble analysis
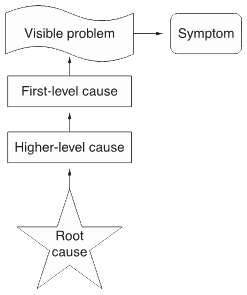
Root Cause Analysis Diagram
Conducting Root Cause Assay
When carrying out root crusade analysis methods and processes, it's of import to annotation:
- While many root cause analysis tools tin be used by a single person, the outcome mostly is better when a grouping of people work together to find the problem causes.
- Those ultimately responsible for removing the identified root cause(south) should be prominent members of the assay team that sets out to uncover them.
A typical design of a root cause analysis in an organization might follow these steps:
- A conclusion is made to form a pocket-sized squad to bear the root cause analysis.
- Team members are selected from the business procedure/expanse of the organization that experiences the trouble. The squad might be supplemented past:
- A line managing director with conclusion dominance to implement solutions
- An internal customer from the procedure with problems
- A quality comeback expert in the case where the other team members have little experience with this kind of work
- The analysis lasts most two months. During the assay, equal emphasis is placed on defining and agreement the trouble, brainstorming its possible causes, analyzing causes and furnishings, and devising a solution to the problem.
- During the analysis period, the team meets at to the lowest degree weekly, sometimes 2 or 3 times a week. The meetings are always kept brusque, at maximum two hours, and since they are meant to exist creative in nature, the calendar is quite loose.
- 1 person in the team is assigned the office of making certain the analysis progresses, or tasks are assigned to diverse members of the squad.
- Once the solution has been designed and the determination to implement has been taken, it can take anywhere from a solar day to several months before the change is complete, depending on what is involved in the implementation process.
Root Cause Analysis Resources
You lot can too search articles, case studies, and publications for RCA resources.
Books
The ASQ Pocket Guide to Root Cause Analysis
Root Cause Analysis: The Core of Trouble Solving and Corrective Activity
Root Cause Assay: Simplified Tools and Techniques
Data Quality: Dimensions, Measurement, Strategy, Management, and Governance
Articles
The Art of Root Cause Assay (Quality Progress) Five whys analysis is the art of systematically drilling down to a real root cause. Substantially, you lot can detect the root cause of a problem and show the relationship of causes by repeatedly asking the question, "Why?"
Under Scrutiny( Quality Progress ) A new definition of root cause could help people realize a systematic procedure beyond cause and effect is needed for root cause analysis.
Digging For the Root Cause (Half dozen Sigma Forum Magazine) At the philosophical level, there is no absolute root crusade in the infinite concatenation of causation. With this concept in mind, the challenge is to know when to stop drilling down and conclude the root cause has been reached. In Six Sigma training at that place are three keys that tin can help attain that finish, which this article explores.
Instance Studies
The Touch Of Human Factors On Lead Fourth dimension (Journal for Quality and Participation) EDR, a provider of belongings management software solutions, applies the DMAIC process to uncover and accost the root causes of a customer lead time problem.
Using Exploratory Data Assay To Improve The Fresh Foods Ordering Procedure In Retail Stores (PDF) This case report demonstrates how explorative data analysis, root cause analysis, and basic statistics helped reduce the inefficiencies in the retail inventory and ordering process of fresh foods within grocery chains.
Webcasts
Root Cause Analysis for Beginners, Part 1 Jim Rooney, an ASQ Fellow and quality veteran with more than 30 years' feel in numerous industries, walks through the basics of root cause analysis in this showtime of a two-part webcast series.
Root Cause Assay for Beginners, Office two Jim Rooney, an ASQ Fellow and quality veteran with more than than 30 years' experience in numerous industries, walks through the basics of root cause analysis in this 2nd of a two-part webcast serial.
Getting The Defects Out Of Root Crusade Assay In this 50-infinitesimal presentation, author Duke Okes introduces root cause assay, covering topics including defining important terminology, describing types of causes, determining how deep to take an investigation, defining the trouble clearly, and more.
Certification
- Manager of Quality/Organizational Excellence – CMQ/OE
- Vi Sigma Green Belt – CSSGB
- 6 Sigma Black Chugalug – CSSBB
- Quality Process Annotator – CQPA
- Quality Improvement Associate – CQIA
Courses
- Root Cause Analysis
- Root Cause Analysis: Solve Bug by Eliminating Causes
Adapted from Root Cause Analysis: Simplified Tools and Techniques and Root Crusade Analysis: The Core of Problem Solving and Cosmetic Activeness, ASQ Quality Press.
Source: https://asq.org/quality-resources/root-cause-analysis
0 Response to "what would be your approach to finding the root cause of a problem?"
Post a Comment